Sharon Vaughn, Leticia Martinez, Kelly J. Williams, Jeremy Miciak, Anna-Maria Fall, & Greg Roberts
PDF Version
How does an intensive reading intervention affect the reading achievement of ninth-grade English learners with reading difficulties?
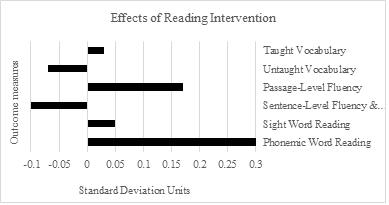
Some English learners (ELs) in ninth grade have difficulty comprehending grade-level text, preventing them from learning content in other subject areas. To address this we implemented an intensive, multicomponent reading intervention for one year with ninth-grade ELs with reading difficulties. The intervention was provided in addition to core instruction and focused on word-reading, fluency, vocabulary, comprehension. Foundational skills and strategies were taught through explicit instructional methods, and students worked in cooperative learning groups to apply these skills and strategies to content area texts. ELs who received the reading intervention performed better on some measures of reading achievement (sentence-level fluency and comprehension, taught vocabulary words) than ELs who did not receive the reading intervention. On other measures, there were not substantial differences between the two groups (word-reading, untaught vocabulary words, and text comprehension).