Effect of Active Learning Professional Development Training on College Student Outcomes
Is there an effect of participating in Active Learning Professional Development (ALPD) training on student performance?
Students who took a course with an ALPD instructor were three percentage points more likely to take additional classes in the same subject area compared to students who were taught by non-participant. Non-participants persisted at a rate of about 68%, so a three percentage point increase represents a 5% improvement. Importantly, ALPD training is related to higher likelihood of implementing active learning instructional practices in the classroom. We do not find any differences in students’ current course grade or performance in the next class.
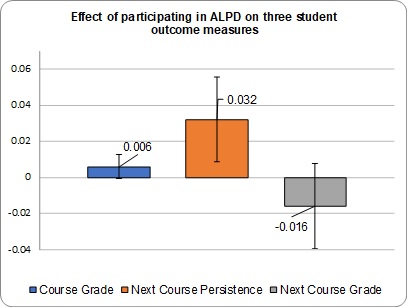
How to read this chart: This figure shows that students who took a course with an ALPD trained instructor were three percentage points more likely to take another course in the same field of study in the immediate next term (p<0.05). No clear difference in course grades was evident either in the ALPD-instructed course, or in the next course taken.
What is Active Learning Professional Development training?
The Active Learning Professional Development training was implemented at a large public research university and was open to faculty across all disciplines. It included eight 90-minute weekly sessions in which faculty worked to increase active learning in their instructional materials under the guidance of an expert facilitator. Each session included a short lecture, assignments, and several readings related to topics in that session. Some of the key topics covered include the role of assessment, different forms of feedback, strategies to increase inclusivity, linking course goals with assignments and activities, and leveraging technology.
How did we do this study?
The study was made possible using university records of students and instructors between fall 2016 through winter 2020. We compared student performance of the same instructor before and after the ALPD training while comparing student performance across sections of the same course. When looking at next course grade, we compared grades of students in the same next class to address concerns than the learning experiences in a course may influence a students’ subsequent course choice. Our sample includes 1,464 instructors who taught 697,715 students across sections and terms. Among these instructors, 105 instructors finished the ALPD training at the time of this study.
We also obtained classroom observation data of 392 classes to examine the association between active learning training and the likelihood of implementing active learning instruction in the classroom.
Finally, we note that a small number of participants have participated in ALPD which potentially limits the conclusion we can draw on the positive effect of the training on student outcomes and encourage future studies to build upon these findings.
Full Article Citation:
Park, E.S. & Xu, D. (2022). The effect of Active Learning Professional Development training on college students’ academic outcomes. Journal of Research on Educational Effectiveness, https://doi.org/10.1080/19345747.2022.2151954.
